CS/클라우드컴퓨팅
14. Container
호프
2023. 12. 7. 15:40
Container
Disadvantages of Virtual Machines
Pros
- Full autonomy(자율성)
- Very secure
- Lower costs
- Used by all cloud providers for on demand server instances
Cons
- Not very portable since size of VMs are large
- Overhead
Container

Container
- cut down VMs used to execute code in an isolated environment
- portable and lightweight
- fully packaged software with all dependencies included
- can be used for development, training, and deployyment
- easily share containers
Linux Containers
- Run everywhere: regardless of kernel version / host distro
- Run anything: if it can run on a Linux kernel, it can run
- Lightweight VM
- own process space / network interface
- can run stuff as root (root권한으로 프로그램 실행 가능)
- no device emulation (실제 하드웨어 디바이스 직접 사용)
- Container == isolated processes
- but share kernel wit host
What Makes Containers so Small?
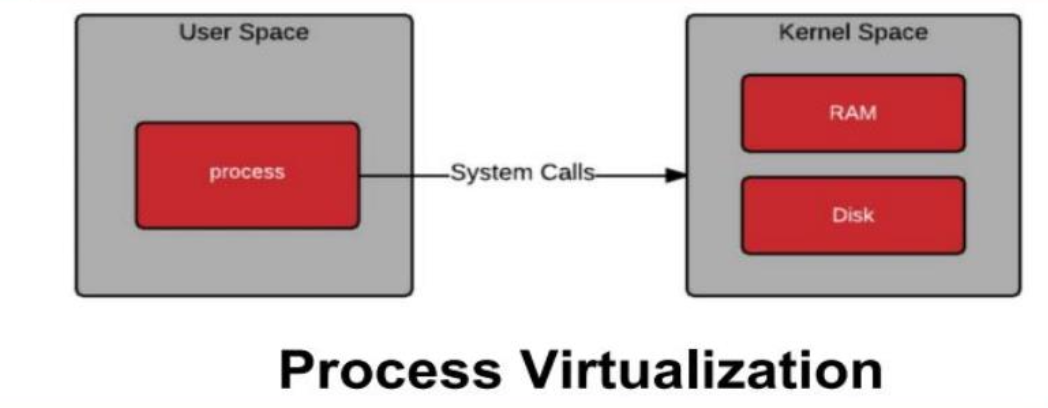
- Container == user space of OS
- User space: all of the code in an OS that lives outside of the kernel
Docker
Docker

Docker
- open source platform for building, deploying, and managing containerized applications
Docker Image
- basis of a Docker container
- represent a full application
- template like a blueprint to create a running Docker container
Docker Container
- standard unit in which the application service resides and executes
Docker Image = recipe, Docker Container = dish
Docker Engine
- creates, ships and runs Docker containers
Registry Service (Docker Hub or Docker Trusted Registry)
- cloud or server-based storage and distribution service for your images
Dockerfile
FROM alpine:latest
RUN apk update
RUN apk add nmap
ENTRYPOINT ["nmap"]
CMD ["localhost"]FROM
- tells the daemon, which base image to use while creating our new Docker image
- you can use alpine, Ubuntu, Fedora, or any other OS image
RUN
- instructs the Docker daemon to run the given commands while creating the image
- Dockerfile can have multiple RUN commands, each of these RUN commands create a new layer in the image
ENTRYPOINT
- let your container to run the same executable every time
CMD
- set default commands and/or parameters when a docker container runs
- CMD can be overwritten from the command line via the docker run command
Multiple Containers from Same Image
- You can run multiple containers from the same image
- Those containers are not necessarily all identical
- You can instantiate it with different parameters using the CMD and therefore different containers will be different
Docker Image Layering
- When execute the build command, the daemon reads the Dockerfile and creates a layer for every command
Image Layering
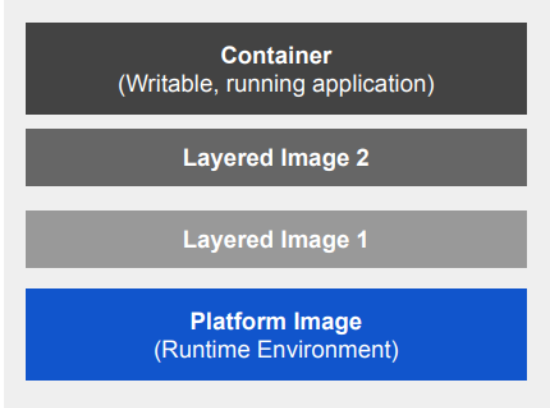
- A application sandbox
- Each container is based on an image that holds necessary config data
- When you launch a container, a writable layer is added on top of the image
- A static snapshot of the container configuration
- Layer images are read-only
- Each image depends on one or more parent images
- An Image that has no parent
- Platform images define the runtime environment, packages, and utilities necessary for containerized application to run
Docker Running Commands
docker --version- get version of Docker CLI
docker container ls
docker image les- list all containers & images
docker build -t ac215-d1 -f Dockerfile .- build an image based on a Dockerfile
-t ac215-d1: name of the image-f Dockerfile .: name of the dockerfile and "." means look at the current working directory
docker run --rm --name ac215-d1 -ti --entrypoint /bin/bash ac215-d1- run a docker container using the image from Docker Hub
--rm: automatically clean up the container and remove the file system when the container exit--name ac215-d1: name of the container-ti: t - give us a terminal, i - interactive mode--entrypoint /bin/bash: default command to execute on startupac215-d1: name of the image to use
docker system prune -a- exit from all containers and let us clear of all images
system: docker command for systemsprune -a: docker command option to remove all images not referenced by any containers
Why use Containers?
- We need to handle many payloads meaning that we need different language supports
- We need to deploy on many targets meaning that we need to deploy on different OSes
- 👉 You can solve this problem by using containers
Monolithic Architecture: traditional model
Pros
- Simple to develop, test, and scale
Cons
- Difficult to maintain
- One component failure will cause whole system fail
- Difficult to create the patches for monolithic architecture
- Adapting to new technologies is challenging
- Take a long time to startup because all components needs to get started
👉 Today: Microservice Architecture
Software Development Workflow
Software Development Workflow without Container
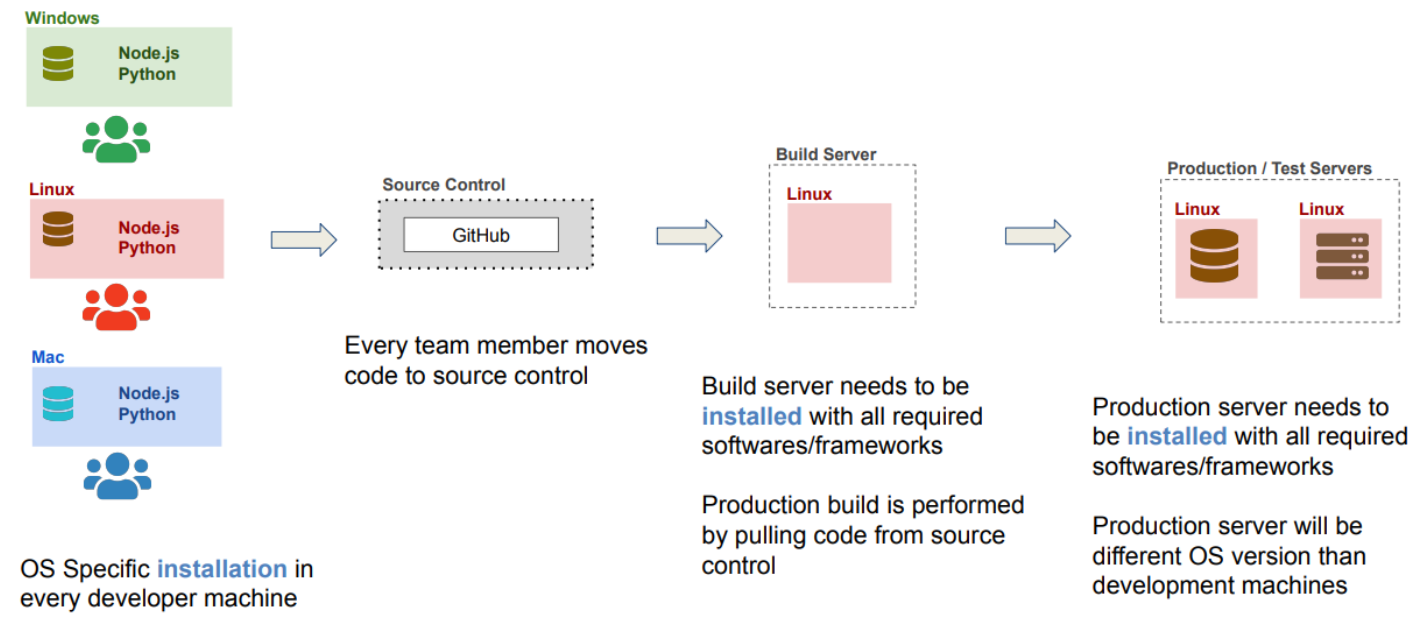
Software Development Workflow with Container

Container Orchestration
Container Orchestration
Container Orchestration
- underlying platform with a set of resources
- orchestrate the connectivity btw the containers and automataically scale up and down based on the load
- whole process of automatically deploying and managin containers
Kubernetes (K8s)
- open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications
- groups containers that make up an application int logical units for easy management and discovery