[Ch5] ICMP, SDN, SNMP
ICMP
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
ICMP: Internet Control Message Protocol
- used by hosts & routers to communicate network-level information
- error reporting
- 중간 라우터에서 incoming pkt에 문제 발생 시, ICMP msg를 생성하여 해당 pkt의 src host로 전송한다.
- network-layer above "IP": ICMP msgs carried in IP datagrams
- ICMP mesageL type + code + first 8 bytes of IP datagram causing error
- 최종적으로 해당 패킷을 만든 프로세스가 사용하는 포트 번호를 알려주기 위해
- used for traceroute
SDN
NW control app(Routing + NAT, load balancing, firewall, accounting) is programmed as sophisticated SW using high-level API(north bound) at servers which are distinct and remote from [simple & fast] NW devices(packet switch) where the Internet user's traffic go through
SDN (Software Defined Network)
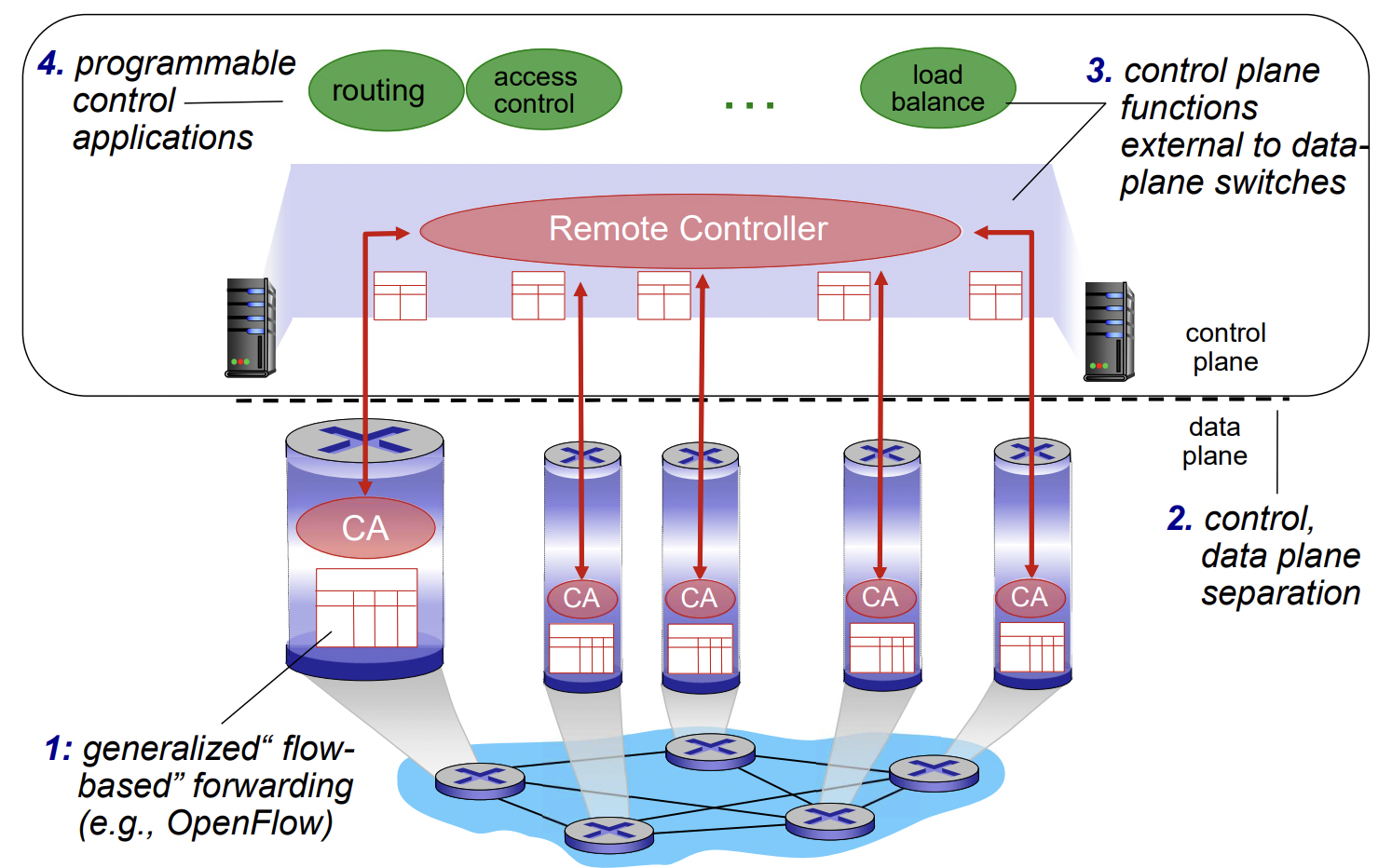
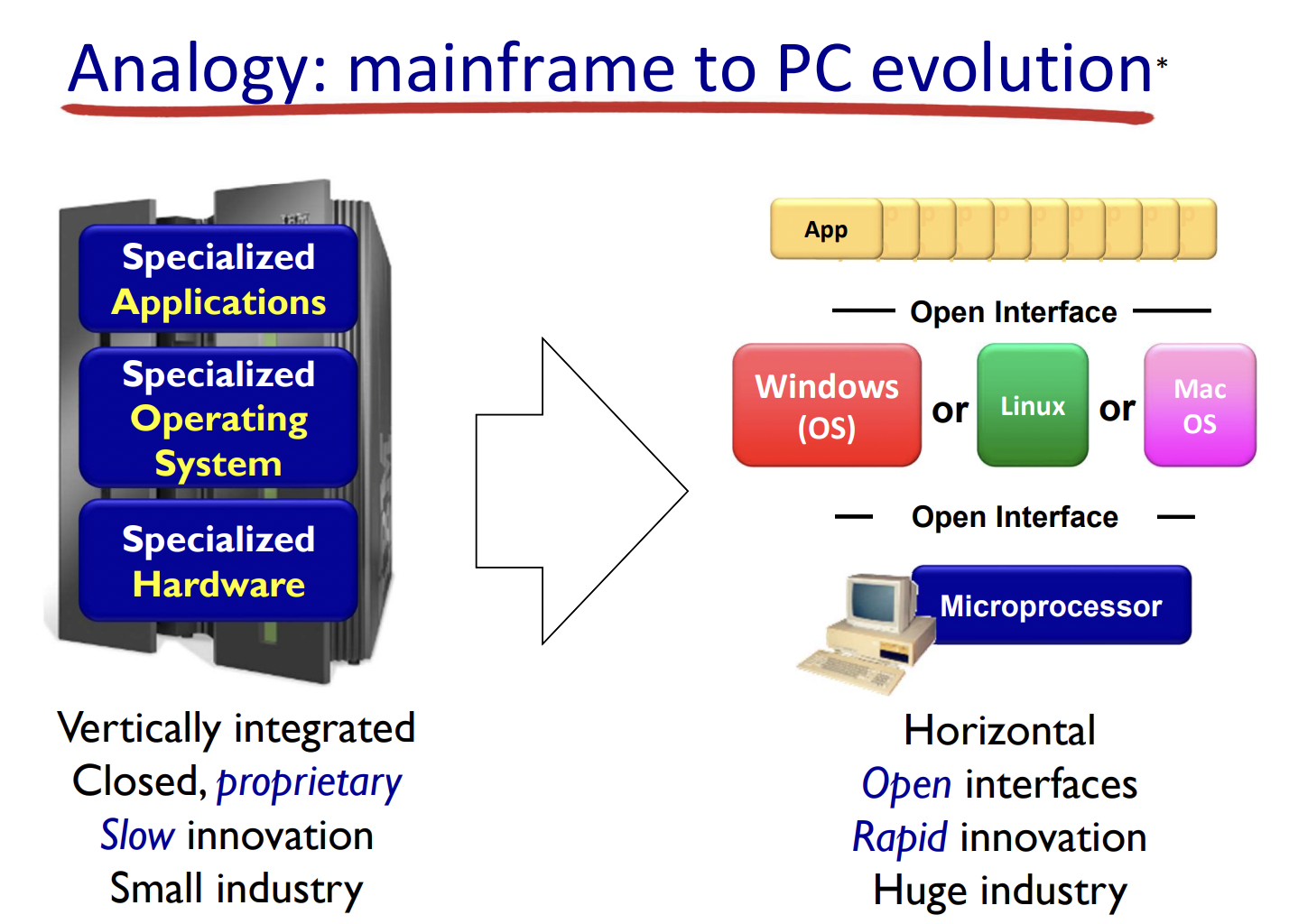
SDN is a framework
- to allow network administrators to automatically and dynamically manage and control
- a large number of entwork devices, services, topology, traffic paths and packet handling (QoS) policies
- using high-level languages and APIs
- multi-tenant environment: SDN controlled NW device
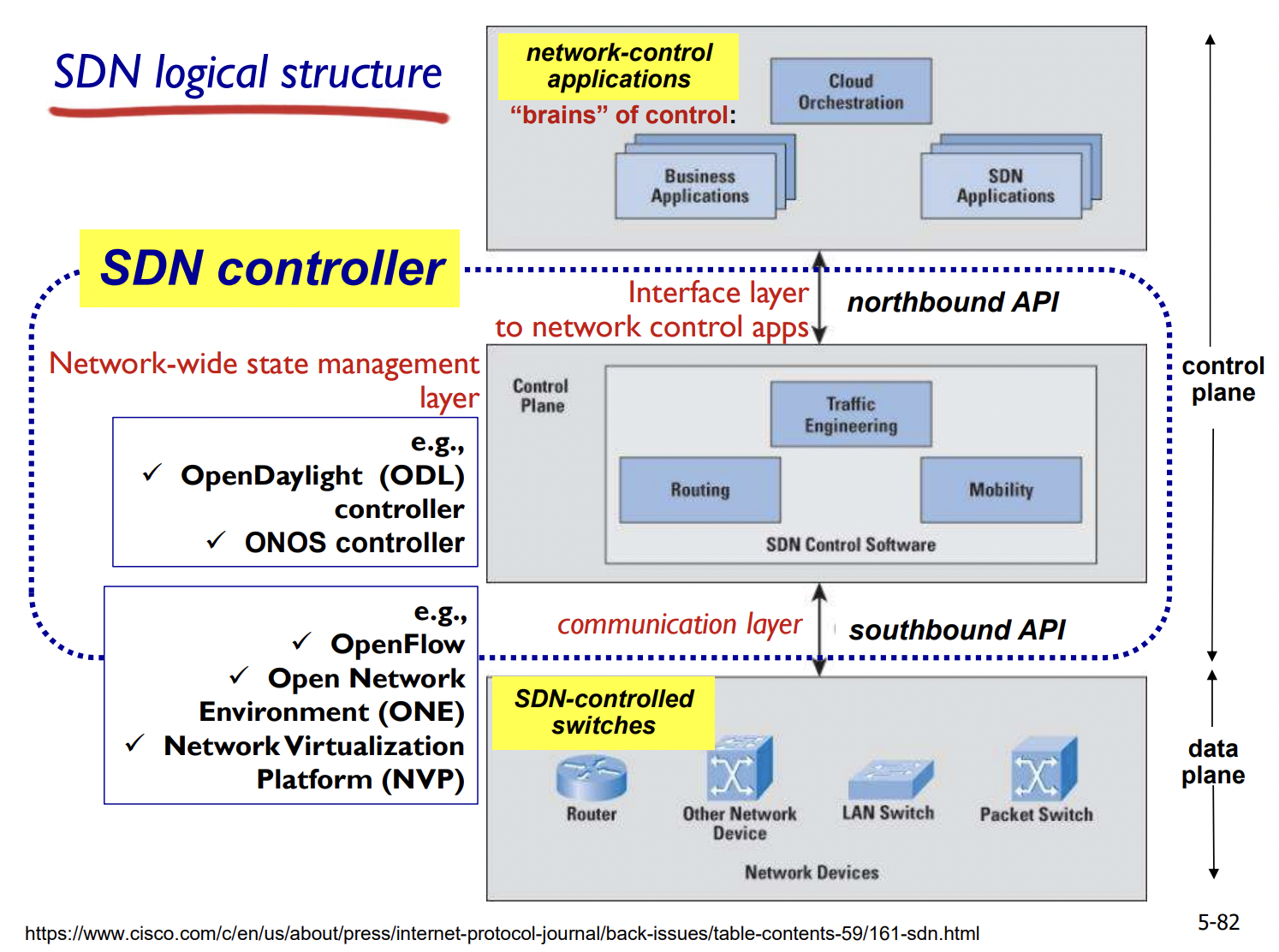
SDN structure
- physical separation of control plane and data plane
- logically centralized control plane(server) controls several routers
- for easier network management, programmable router, open(non-proprietary) implementation of control plane
- 물리적으로는 가입자 패킷이 지나다니는 네트워크 장비의 물리적 분포를 고려해 위치하는 여러 개의 서버들이 logically 하게는 한 개 처럼 동작
- SDN에서 라우팅 프로토콜은 SDN Controller에서 동작한다? (X) 👉 라우팅 프로토콜을 포함한 다양한 middle box 기능들은 최상의 network control app에 해당한다. SDN Controller는 실제 가입자 패킷이 지나다니는 HW 장비의 자원을 관리하여 상위 app에 알려주는 역할을 한다.
SDN: Data plane switches
- fast, simple, commodity switches implementing generalized data-plane forwarding in hardware
- southbound API (e.g. OpenFlow) for communicating with controller
- switch flow table computed by controller
SDN: Network control applications
- brains of control: implement control functions using northbound API provided by SDN controller
- can be provided by 3rd party: distinct from SDN controller
- routing protocol을 포함한 다양한 middle box 기능들을 수행
SDN: SDN Controller (Network OS)
- maintain network state information (switch가 알려줌) -> 상위 application에 전달
- interacts with network control applications via northbound API
- interacts with network switches via southbound API
- implemented as distributed system
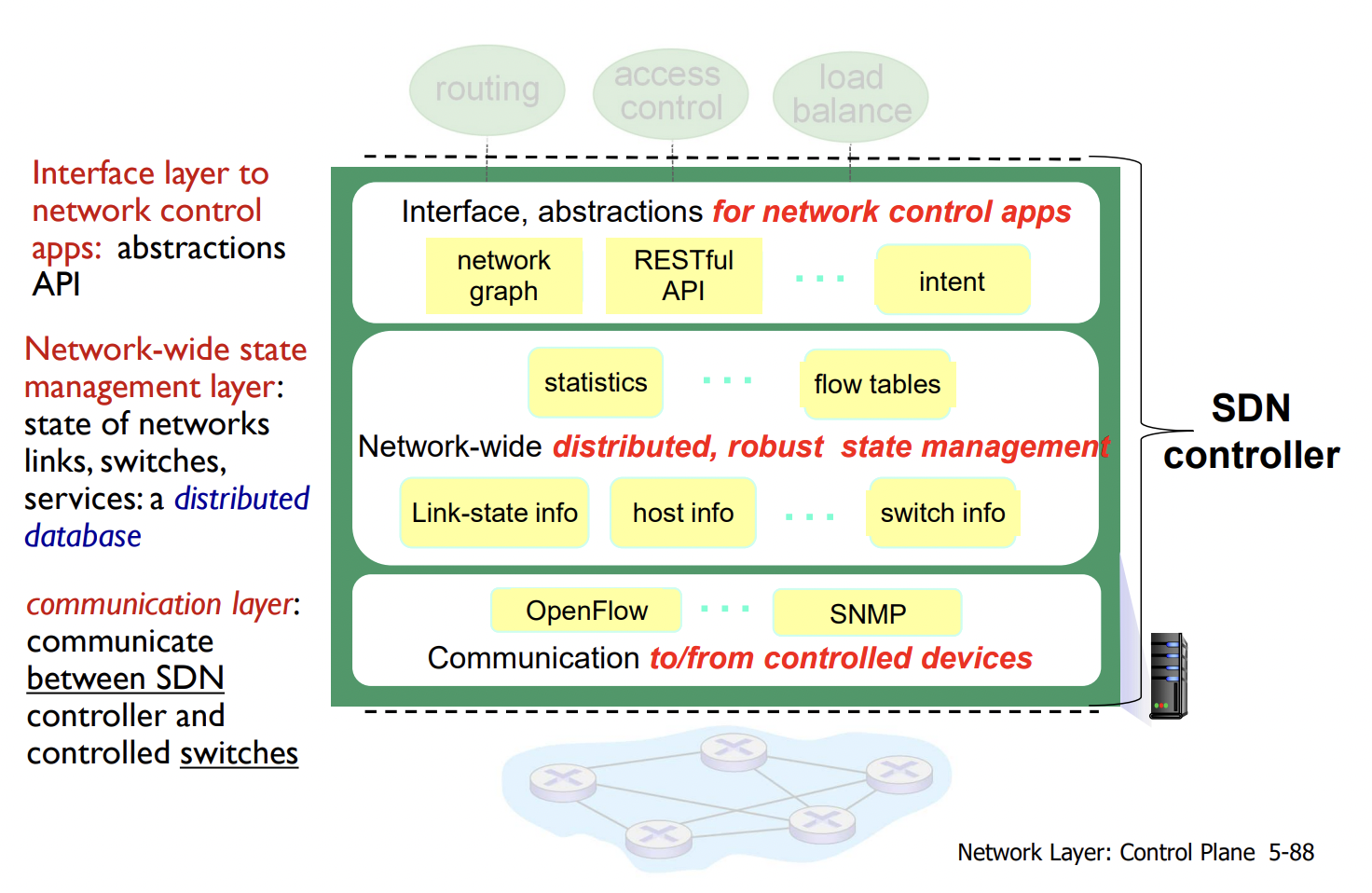
- SDN은 least-cost path 외에 운영자가 원하는 특정한 e2e path 설정 가능
- flow table은 northbound 위의 app에서 SDN Controller 로부터 정보를 받아서 생성, 변경된다.
OpenFlow
OpenFlow protocol
- operates btw controller and switch (southbound API)
- using TCP to exchange messages
- three classes of OpenFlow messages
- controller-to-switch
- switch-to-controller
- symmetric
OpenFlow: controller-to-switch msg
- feature: controller queries switch featrues, switch replies
- configure: controller queries/sets switch configuration parameters
- modify-state: add, delete, modify flow entries in the OpenFlow tables
- packet-out: controller can send this packet out of specific switch port
OpenFlow: switch-to-controller msg
- packet-in: transfer packet to controller
- flow-removed: flow table entry deleted at switch
- port status: infrom controller of a change in port status
SDN Controller(network operator) don't program switches by creating/sending OpenFlow msgs directly
👉 Instead, use higher-level abstraction (northbound API) at controller == Network control applications
NFV (Network Function Virtualization)
SDN
- Internet-scaling: SDN은 scalability의 challenge가 있어 특정 목적을 가진 망에 적합함
- reliable distributed system for control plane
- networks, protocols meeting mission-specific requirements: real-time, ultra-reliable, ultra-secure ..
NFV (Network Function Virtualization)
- destination-based forwarding에 기반한 라우팅 기능을 virtualization하는 것이므로 SDN 처럼 다양한 path 설정은 불가능하다.
- separation of HW and function
SNMP
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
Network Management
- requiring monitoring, control
- deployment, integration, coordination of the HW, SW, and human elements
Infrastructure for Network management
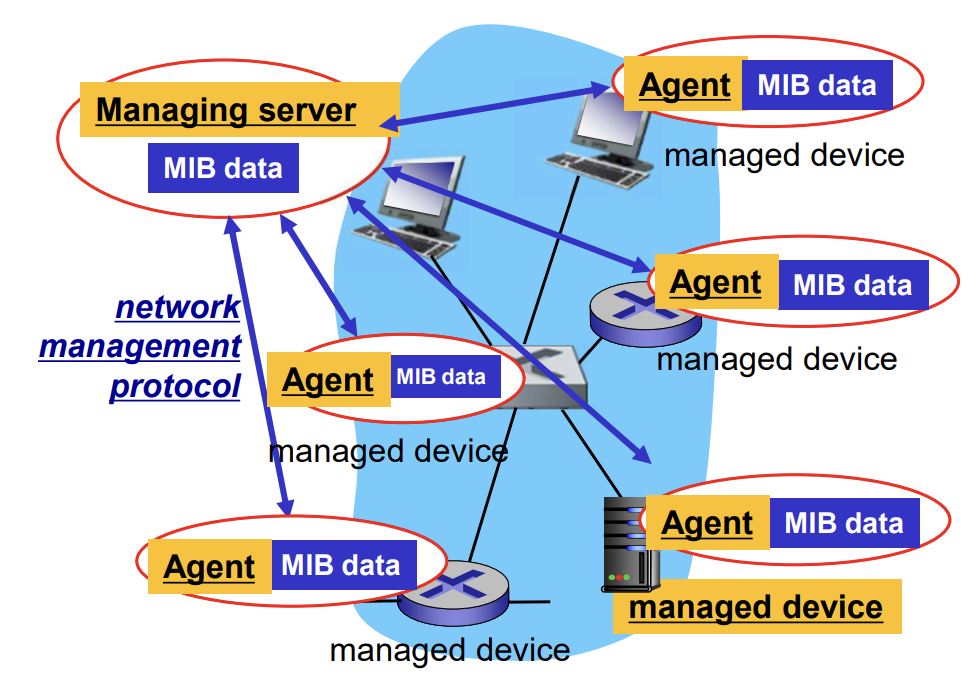
- managing server
- managing device
- MIB (Management Information Base)
- network management protocol (= SNMP)
- managed devices contain managed objects whose data is gathered into a MIB
SNMP는 네트워크 장비를 관리, 제어하기 위해 관리 서버와 관리 대상 agent 간에 주고받는 프로토콜로, 정기적으로 간단한 정보를 교환하는 방식이므로 초기 연결 지연이 없는 UDP를 사용한다.
SNMPv2 (RFC 3415) protocol
- Application-layer (L5) protocol on UDP (ports 161, 162)
- to convey network-management control and information msgs
- btw a managing server and an agent
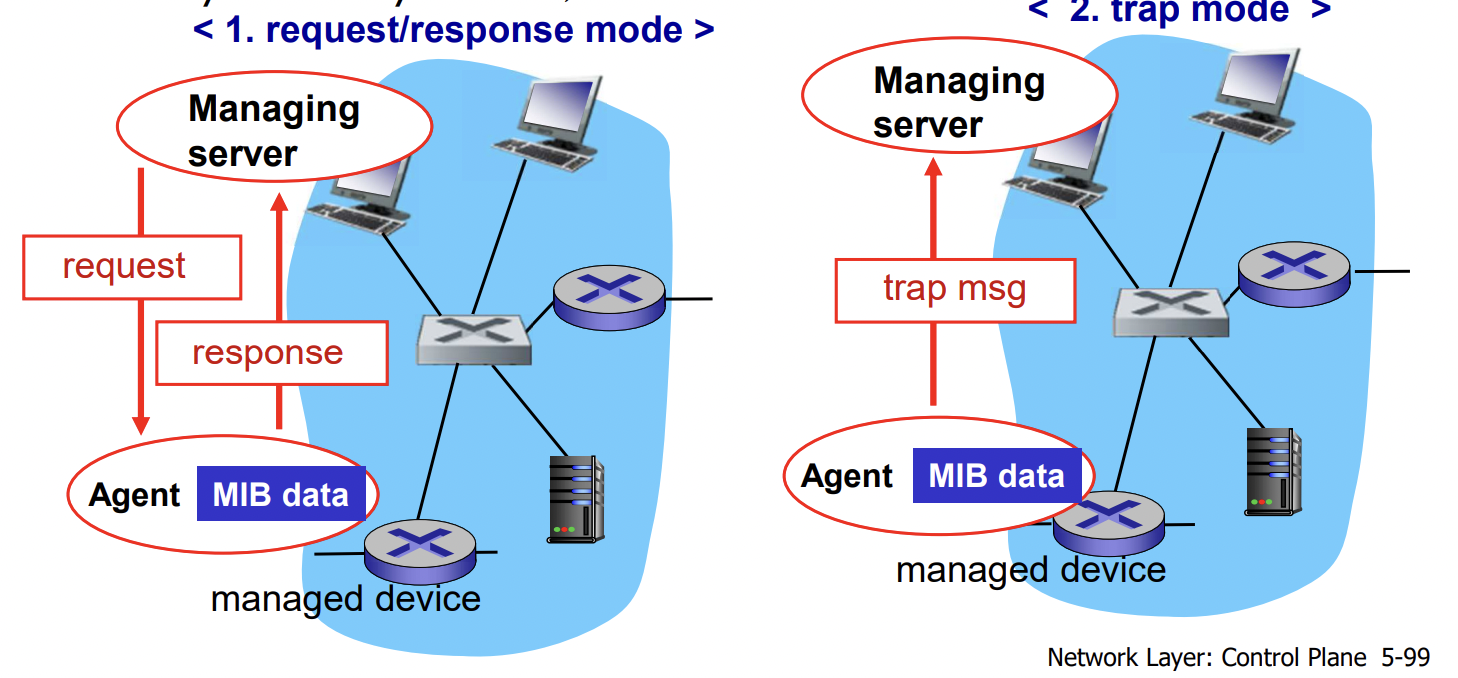
- Two ways to convey MIB info, commands
- request/response mode
- trap mode
Chapter 5 Summary
- Approaches to network control plane
- per-router control (traditional)
- logically centralized control (SDN; software defined networking)
- Traditional routing algorithms
- implementatino in Internet: RIP, OSPF, BGP
- ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
- SDN controllers
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)