[Ch6] Link Layer
Link Layer Services
Link Layer

- 1 subnet & 4 L2-switch (no IP addr, no MAC addr)
Link Layer (Layer 2)
- nodes: hosts and routers
- links: communication channels that connect adjacent nodes along communiation path - wired & wireless links
- layer-2 packet == frame that encapsulates datagram
Data Link Layer (Layer 2) has responsibility of transferring datagram from one node to physically adjacent node over a link (each node has L3)
Where is the Link Layer Implemented
- Link layer is implemented in each and every host in adapter (aka. network interface card; NIC)
- Ethernet card(802.11)
- implements link, physical layer
- Link layer is combination of hardware, software, firmware
Link Layer Services
Framing
- encapsulate datagram into frame, adding header (src/dst MAC addr)
Link Access
- channel access if shared medium
Reliable delivery btw adjacent nodes
- flow control: pacing btw sending & receiving nodes
- error detection: receiver detects presense of errors and signals sender for retransmission or drops frame
- error correction: receiver identifies and corrects bit errors without resorting to retransmission
Multiple Access Link
Multiple Access Link: 2 Typs of Link
Point-to-Point networks (typically WAN)
- pairs of host (or routers) directly connected
- ex) p2p link btw Ethernet switch and host
Broadcast networks (typically LAN)
- all hosts (or routers) share a single communication channel
- ex) old fashioned Ethernet, Wi-Fi, Satellite networks, HFC (Hybrid fiber-coaxial cable)
- L2 Switch: Buffer O -> 포트마다 다른 BW 가지는 링크 연결 가능
- Hub: Buffer X -> flooding, 모든 포트에 연결된 링크의 BW가 동일해야 함
Multiple Access Protocol
Due to a single shared broadcast channel:
👉 two or more simultaneous transmissions by nodes: interference
👉 collision if node receives two or more signals at the same time
👉 Why we need Multiple Access Protocol
Multiple Access Protocol
- distributed algorithm that determines how nodes share channel (i.e. determine when node can transmit)
- channel particioning
- by time (TDMA), frequency (FDMA) or code (CDMA)
- random access (dynamic)
- Collision Detection (CD): CSMA/CD used in Ethernet (IEEE 802.3)
- Collision Avoidance (CA): CSMA/CA used in 802.11 (Wi-Fi)
- taking turns
- bluetooth, FDDI, token ring
Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
- transmission time (L/R) 동안 listen -> collision detection 가능
Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA)
- CTS, RTS 보내서 충돌이 일어나지 않도록 선점
- AP 하고만 통신 -> detection 불가 (Hidden node problem)
Hidden node problem: wireless network에서 두 노드 A, B가 공통으로 통신이 가능한 노드 P가 있는데 A와 B는 통신 거리(radio range) 밖에 있거나 두 노드 사이에 장애물이 있어 서로의 신호가 P에서 충돌하는 것을 감지 (Collision Detection)할 수 없는 현상
MAC addresses and ARP
IEEE 802 Standard
IEEE 802
- a family of standards for LANs which defines
- Logical Link Control (LLC) - OS
- Several Media Access Control (MAC) sub-layers - HW, NIC

MAC Address (or LAN address)
32-bit IPv4 address
- Network Layer (L3) address for interface used for layer 3 forwarding
MAC address (== LAN or physical or Ethernet address)
- 48-bit MAC address burned in NIC
- permanent, unique, IEEE manages the MAC address space
- no hierarchical structure (same MAC address can be used no matter where the computer goes)
- 16진수로 표현 (ex. FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF: broadcast MAC addr)
- 두 호스트를 연결하는 e2e path에서 경유하는 라우터들은 모두 동일한 src IP addr와 dst IP addr를 보고 라우팅을 결정한다.
- 어떤 NIC 카드에 할당된 L3 IP 주소는 위치에 따라 변하는 주소이나, L2 MAC 주소는 변하지 않는다.
- IP address = postal address / MAC address = social security number
ARP: Address Resolution Protocol
ARP Table
- each IP node (host, router) on LAN has ARP table
- 특정 NIC에 설정된 IP address와 MAC address의 매핑 테이블
- <IP addr; MAC addr; TTL>
- TTL (Time to Live): time after which address mapping will be forgotten (typically 20 min)
In case of Same LAN (A wants to send datagram to B & B's MAC address not in A's ARP table)
- A broadcasts ARP query packet, containing B's IP address
- broadcast: dest MAc address = FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
- all nodes on LAN receive ARP query
- B receives ARP pkt and replies to A with its (B's) MAC address
- frame sent to A's MAC address (unicast)
- A caches (saves) IP-to-MAC address pair in its ARP table until information becomes old (time out)
- <IP addr; MAC addr; TTL>
- ARP is plug-and-play
- nodes create their ARP table without intervention from network administrator
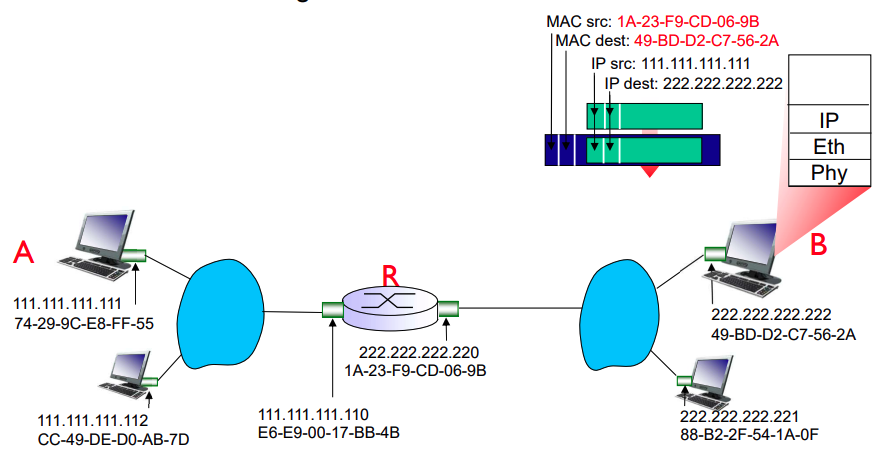
In case of Routing to another LAN
- walkthrough: send datagram from A to B via R
- 두 host를 연결하는 e2e path에서 한 hop을 지날 때 2계층 주소는 계속 바뀌지만 3계층 주소는 동일