-
Reliability and Availiability
-
Service Availability
-
Availability Metrics
-
Service Reliability
-
Failure types
-
Failure
-
Failure types
-
Service-Level vs Machine-Level Failure
-
Hardware Failure and Software Failure
-
Other types of Failure
-
Features for Reliability
-
Hardware Features for Reliability
-
Service Level Agreement(SLA)
Reliability and Availiability
Service Availability
Service availability
- $ Availability = \frac{Uptime}{Uptime + Downtime}$
- $ Availability = \frac{TotalInServiceTime - Downtime}{TotalInServiceTime} $
- calculate availability based on service downtime
- $ Availability = \frac{MTBF}{MTBF + MTTR} $
- Service availability ratings are commonnly quantified as number of nine's (9)
Availability Metrics
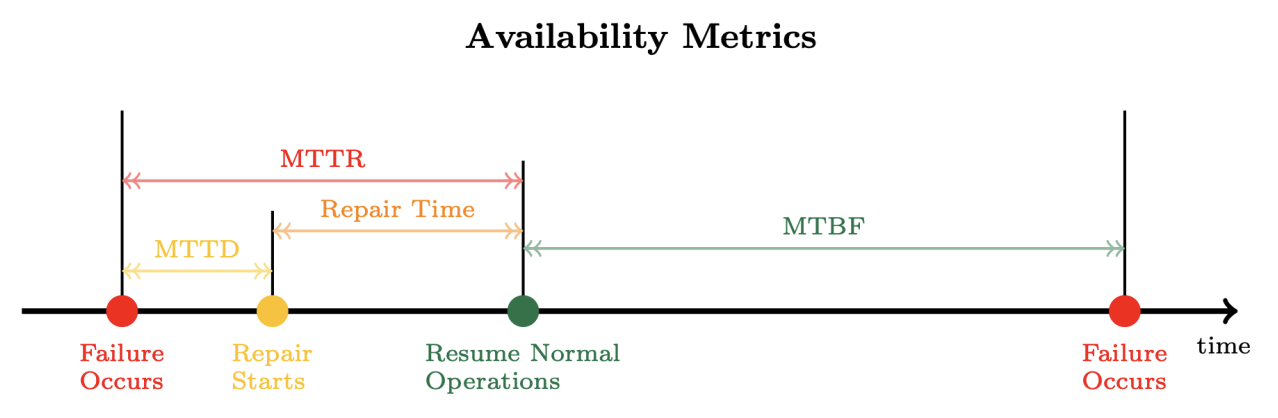
Mean time between failure (MTBF)
- average time btw when a workload begins normal operation and its next failure
Mean time to repair(recovery) (MTTR)
- period of time when the workload is unavailable while the failed subsystem is repared or returned to service
Mean time to detection (MTTD)
- amount of time btw a failure occuring and when repair operations begin
Availability with Redundancy
Service Reliability
Reliability
- defined as the ability of an item to perform a required function under stated conditions for a stated time period
- $ Service Reliability = \times{\frac{Successful Responses}{Total Requests}}{100%} $
- more convenient to focus on the much smaller number of unreliable service defects since most services are very reliable
- $ DPM = \times{\frac{Unsuccessful Requests}{Total Requests}}{100%}$
- DPM = Defects per million
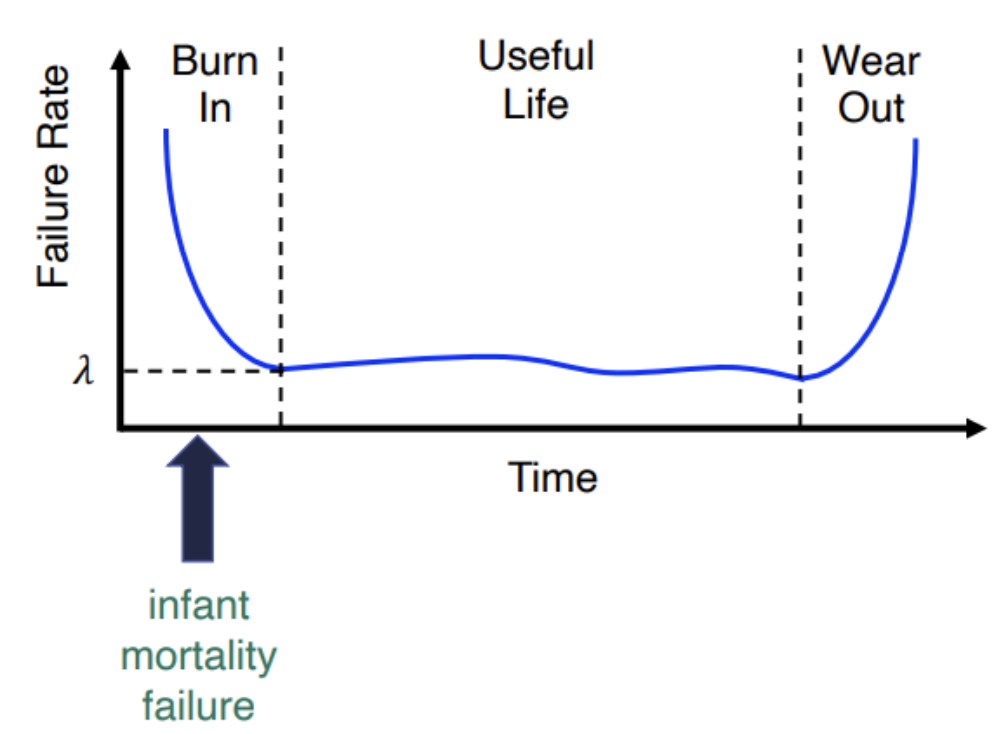
Reliability Curve
- The bathtub curve
- The failure rate of a system usually depends on time
Failure types
Failure
Failure
- evnet that makes a system fail to operate
- failures are inevitable in complex system
- failures can impact the service deliverd to users
- servie response time can degrade
- isolated service requests can fail to respond within an acceptable time
- repeated service requests can fail
Failure types
Permanent faults (hard error)
- A continuing error
- Caused by some physical failures
Temporary faults
- Transient fault (soft error) leads to independent one-time errors
- Intermittent faults occur due to a weak system component
Service-Level vs Machine-Level Failure
Service-Level Failure
- 특정 서비스가 사용 가능한 기간 동안 정상적으로 동작하지 않는 상황
- Operator-caused or misconfiguration errors are the largest contributors
- Hardware-related faults only 10-25% of the total failure events
- But this is because fault-tolerant techniques implemented in hardware
- It is harder to tolerate general software bugs or operator mistakes than known hardware failure patterns
Machine-Level Failure
- 전체적인 시스템 또는 장치가 작동하지 않는 상태
Hardware Failure and Software Failure
Hardware Failure
- Processor errors: aging
- DRAM soft erros: leakage power
- DRAM hard errors: radiation from the universe during delivery
- Disk errors (the most dominant reason of failures in datacenter)
- typically ranged btw 2 ~ 4%
- disk can crash
- Hydrophilic dust
- Network failure due to communication channel breaking
- Random failures from manufacturing defects
Software Failure
- major reason = upgrades
Other types of Failure
Cloud Management System (CMS) Failures
- Overflow: if the queue is full, new requests will be dropped
- Timeout: when waiting time of the queued requests is over the due time
- Data resource missing: when some data are removed but the data resource isn't updated
- Computing resource missing: turning off the PC without notifying the CMS
Security Failure
- Customer faults: about 95% of failures
- Software breaches: when attackers can gain access to the customer information
- Security policy failures
Human Operational Faults
- Misoperation: accidental faults made by human personnel operating
- Misconfiguration: network node software, cloud management software is misconfigured
Environmental Failure
- Environmental disasters: main role in the dependability of cloud system
- Cooling system failure: servers will shut down completely or be under-utilized regarded as unavailable
Features for Reliability
Hardware Features for Reliability
Hardware Features for Reliability
- Processor
- error detection with instruction retry
- errors detected by residue checking
- Memory
- parity or ECC protection of memory componenets
- redundant array of independent memory
- Storage
- RAID configuration
- journaling file systems for file repair after crashes
- checksums on both data and metadata
- System
- hot swapping of components
- partitioning, virtual machines
Mitigating Hardware Failures via Virtualization
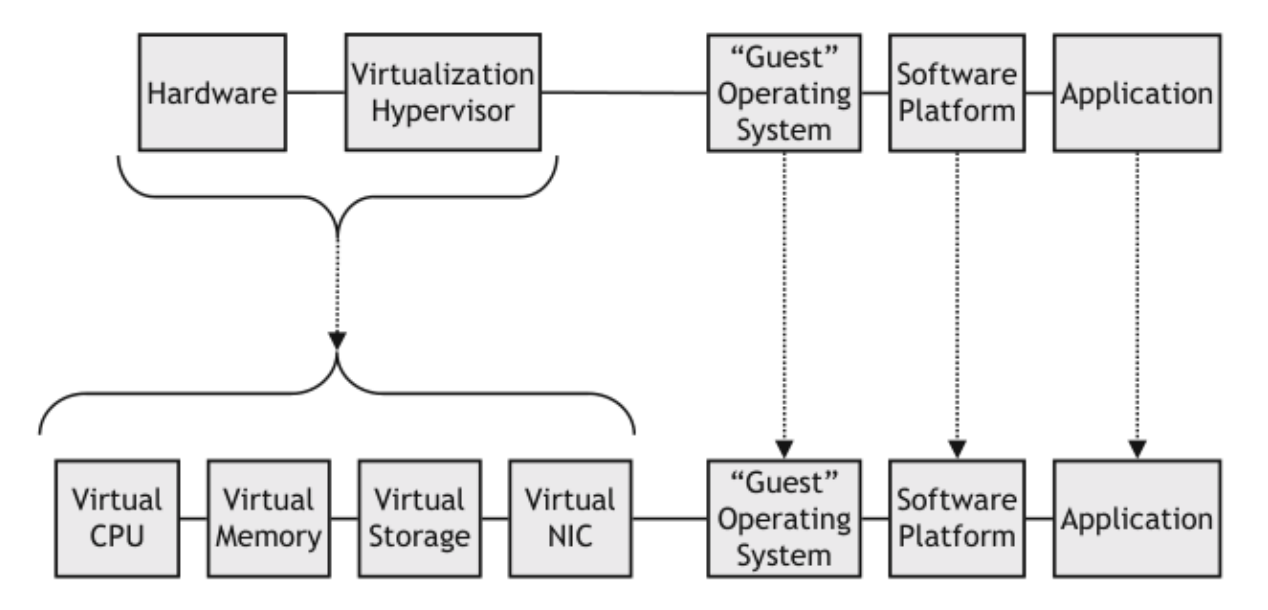
- Virtualization layer of softawre decouples the VM instance from the physical hardware
- Virtual CPU
- abstraction of the available physical CPUs or processor cores
- Virtual CPU can be used by the hypervisor to mitigate the impact of a single physical CPU failure
- If failure in physical CPU -> rellocate another physical CPU resources to the affected virtual CPU, and restart VM
- Virtual NIC
- NIC (network interface card): hardware component that connects the host computer to the external network
- Virtual NIC provide abstraction of that physical component to gestOS by mapping to a physical NIC or to a virtual network
- VM can be configured to multiple physical NIC's via their virtual NICs
Service Level Agreement(SLA)
Service Level Agreement (SLA)
- SLA serves as the blueprint and warranty for cloud computing services
- document specific parameters minimum service levels and remedies for any failure to meet the specified requirements
- determine the pricing model and payment terms
- describe QoS features, guarantees and limitations of one or more cloud-based IT resources
- use. service quality metrics to express measurable QoS characteristics
- Availability, reliability, performance, scalability, resiliency (elasticity)
'CS > 클라우드컴퓨팅' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 17. MapReduce (0) | 2023.12.08 |
|---|---|
| 16. DevOps (0) | 2023.12.08 |
| 14. Container (0) | 2023.12.07 |
| 12, 13. Virtualization (0) | 2023.12.07 |
| 11. Serverless II (0) | 2023.12.05 |
Reliability and Availiability
Service Availability
Service availability
- $ Availability = \frac{Uptime}{Uptime + Downtime}$
- $ Availability = \frac{TotalInServiceTime - Downtime}{TotalInServiceTime} $
- calculate availability based on service downtime
- $ Availability = \frac{MTBF}{MTBF + MTTR} $
- Service availability ratings are commonnly quantified as number of nine's (9)
Availability Metrics
Mean time between failure (MTBF)
- average time btw when a workload begins normal operation and its next failure
Mean time to repair(recovery) (MTTR)
- period of time when the workload is unavailable while the failed subsystem is repared or returned to service
Mean time to detection (MTTD)
- amount of time btw a failure occuring and when repair operations begin

Availability with Redundancy
Service Reliability
Reliability
- defined as the ability of an item to perform a required function under stated conditions for a stated time period
- $ Service Reliability = \times{\frac{Successful Responses}{Total Requests}}{100%} $
- more convenient to focus on the much smaller number of unreliable service defects since most services are very reliable
- $ DPM = \times{\frac{Unsuccessful Requests}{Total Requests}}{100%}$
- DPM = Defects per million
Reliability Curve
- The bathtub curve
- The failure rate of a system usually depends on time

Failure types
Failure
Failure
- evnet that makes a system fail to operate
- failures are inevitable in complex system
- failures can impact the service deliverd to users
- servie response time can degrade
- isolated service requests can fail to respond within an acceptable time
- repeated service requests can fail
Failure types
Permanent faults (hard error)
- A continuing error
- Caused by some physical failures
Temporary faults
- Transient fault (soft error) leads to independent one-time errors
- Intermittent faults occur due to a weak system component
Service-Level vs Machine-Level Failure
Service-Level Failure
- 특정 서비스가 사용 가능한 기간 동안 정상적으로 동작하지 않는 상황
- Operator-caused or misconfiguration errors are the largest contributors
- Hardware-related faults only 10-25% of the total failure events
- But this is because fault-tolerant techniques implemented in hardware
- It is harder to tolerate general software bugs or operator mistakes than known hardware failure patterns
Machine-Level Failure
- 전체적인 시스템 또는 장치가 작동하지 않는 상태
Hardware Failure and Software Failure
Hardware Failure
- Processor errors: aging
- DRAM soft erros: leakage power
- DRAM hard errors: radiation from the universe during delivery
- Disk errors (the most dominant reason of failures in datacenter)
- typically ranged btw 2 ~ 4%
- disk can crash
- Hydrophilic dust
- Network failure due to communication channel breaking
- Random failures from manufacturing defects
Software Failure
- major reason = upgrades
Other types of Failure
Cloud Management System (CMS) Failures
- Overflow: if the queue is full, new requests will be dropped
- Timeout: when waiting time of the queued requests is over the due time
- Data resource missing: when some data are removed but the data resource isn't updated
- Computing resource missing: turning off the PC without notifying the CMS
Security Failure
- Customer faults: about 95% of failures
- Software breaches: when attackers can gain access to the customer information
- Security policy failures
Human Operational Faults
- Misoperation: accidental faults made by human personnel operating
- Misconfiguration: network node software, cloud management software is misconfigured
Environmental Failure
- Environmental disasters: main role in the dependability of cloud system
- Cooling system failure: servers will shut down completely or be under-utilized regarded as unavailable
Features for Reliability
Hardware Features for Reliability
Hardware Features for Reliability
- Processor
- error detection with instruction retry
- errors detected by residue checking
- Memory
- parity or ECC protection of memory componenets
- redundant array of independent memory
- Storage
- RAID configuration
- journaling file systems for file repair after crashes
- checksums on both data and metadata
- System
- hot swapping of components
- partitioning, virtual machines
Mitigating Hardware Failures via Virtualization

- Virtualization layer of softawre decouples the VM instance from the physical hardware
- Virtual CPU
- abstraction of the available physical CPUs or processor cores
- Virtual CPU can be used by the hypervisor to mitigate the impact of a single physical CPU failure
- If failure in physical CPU -> rellocate another physical CPU resources to the affected virtual CPU, and restart VM
- Virtual NIC
- NIC (network interface card): hardware component that connects the host computer to the external network
- Virtual NIC provide abstraction of that physical component to gestOS by mapping to a physical NIC or to a virtual network
- VM can be configured to multiple physical NIC's via their virtual NICs
Service Level Agreement(SLA)
Service Level Agreement (SLA)
- SLA serves as the blueprint and warranty for cloud computing services
- document specific parameters minimum service levels and remedies for any failure to meet the specified requirements
- determine the pricing model and payment terms
- describe QoS features, guarantees and limitations of one or more cloud-based IT resources
- use. service quality metrics to express measurable QoS characteristics
- Availability, reliability, performance, scalability, resiliency (elasticity)
'CS > 클라우드컴퓨팅' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 17. MapReduce (0) | 2023.12.08 |
|---|---|
| 16. DevOps (0) | 2023.12.08 |
| 14. Container (0) | 2023.12.07 |
| 12, 13. Virtualization (0) | 2023.12.07 |
| 11. Serverless II (0) | 2023.12.05 |
