인터넷 개요
What's the Internet?
Nuts and bolts View
Internet: network of networks
- host = end system = end node = termial = station
- protocols control sending, receiving of messages
- Internet standards: RFC, IETF
Service View
- infrastructure that provides services to applicaations
- provide programming interface to application
What's a protocol?
Protocols define format, order of messages sent and received among network entities, and actions taken on message transmission, receipt.
Network Edge (LAN)
Network Edge
hosts: clients and servers
access networks, physical media - wired, wireless communication links
Network Core
interconnected routers, network of networks
End System
end system = hosts: clients and servers
client host와 달리 server host는 core network의 라우터에 직접 연결되어 있다? -> (X)
How to connect end systems to edge router
- residential access net(home network), institutional access net(Ethernet), mobile access net..
Access Network
Access network: 인터넷 호스트(client, server)를 core network의 edge router로 연결해주는 네트워크
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- data transmitted at different frequencies over dedicated line to central office
- use existing telephone line to central office DSLAM
- 구리 전화선을 이용하여 인터넷 연결 제공
- PC 통신 -> ISDN --HFC--> ADSL -> VDSL -> FTTH(fiber to the home)
Cable network
- data transmitted at different frequencies over shared cable distribution network
- HFC: hybrid fiber coax
- homes share access network to cable headened
Host: send packets of data
- 1 large msg -> multiple small packets (L bits each), pkt by pkt으로 독립적으로 전송
- link transmission rate = link bandwidth = link capacity = transmission rate R (bits / sec) bps
Dtrans (transmission delay, sec) = time needed to transmit L-bit pkt into link = L (bits) / R (bits/sec)
Network Core (WAN)
Packet Switching
Packet Switching: hosts break application-layer(L5) messages into packets.
- forward packets from one router to the next, across links on path from source to destination
- each packet transmitted at full link capacity
- statistical TDM - header 필요
Routing
- determines source-destination route taken by packets using routing algorithms (routing table)
Forwarding
- move packets from router's input to appropriate router output
Store-and-Forward
- L-bit 가 모두 들어올 때까지 기다린 후 처리 -> L-bit가 전송되어야 할 정보가 패킷 맨 앞 헤더에 있기 때문
- entire packet must arrive at router before it can be transmitted on next link
- one-hop trasnmission delay = L / R
- end-to-end delay = # of hops * (L / R) when assuming zero propagation delay
Queuing and Loss
If arrival rate to link exceeds transmission rate of link for a period of time:
- packets will queue at output buffer, wait to be transmitted on link
- packets can be dropped (loss) if memorry (buffer) fills up
- because in packet switching, there is no resource (link bandwidth = R) reservation before data delivery
Packet Switching 네트워크를 구성하는 라우터가 Store-and-Forward 방식으로 패킷을 처리하는 동작을 라우터와 L-bit 패킷 입장에서 서술 (패킷은 A 포트에서 들어와서 B 포트로 나간다고 가정)
- L 개의 비트들이 A 포트의 buffer에 저장된다.
- 패킷 헤더를 보고 목적지 주소로 보내기 위해 포워딩 테이블을 검색한다.
- L-bit 패킷이 A에서 B로 스위칭 된다
- L-bit 패킷이 B의 buffer(queue)에 한동안 저장된다.
- L 개의 비트들이 signal로 변환 (transmit) 된다.
Packet Switching에서 메시지를 pkt으로 나누어 전송하는 이유
- 중간 라우터들이 동일한 msg에 속하는 패킷들을 동시에 전송하게 되어 결과적으로 end-to-end delay를 줄이기 위해
- 에러가 있는 링크에서 재전송되는 데이터량을 줄여 링크 사용 효율을 증대시키기 위해
- 여러 사용자가 하나의 링크를 공유할 때 한 명의 사용자가 링크를 오래 점유하는 것을 막기 위해
Circuit Switching
Circuit Switching: end-end resources allocated to, reserved for "call" btw source & destination
- before data delivery, there is call set-up delay -> during data delivery, no processing(routing) at intermediate node
- dedicated resources: no sharing, guaranteed performance, circuit segment idle if not used by call
- commonly used in traditional telephone network
FDM versus TDM
FDM : full rate
Synchronous-TDM: not full rate

Packet Switching VS Circuit Switching
| Packet Switching | Circuit Switching |
|---|---|
| No Call set-up, simpler | Call set-up |
| Allocating link use on demand | Resource reservation |
| Resource sharing | Resource dedicated to a particular user |
| Packet delay or loss | Guaranteed service |
| Queueing delay | Call set-up delay |
| More users can be served | # of users at the same time is limited |
| Good for intermittent, bursty data | Good for apps which require guaranteed bandwidth |
| Dynamic use of BW | Fixed use of BW |
Network Structure
End systems connect to Internet via access ISPs(Internet Service Providers)
- ISP example: T-mobile, SKT, KT, Orange etc.
Access ISPs in turn must be interconnected

Internet exchange point (IXP)
네트워크(ISP)를 연결하는 기술 중 하나로 third-party 회사에서 제공하는 링크를 이용해 다중의 ISP들이 연결되는 방식
- Typically in a stand-alone building with its own switches
- About 300 IXPs in the internet
Peer
네트워크(ISP)를 연결하는 기술 중 하나로 동일 계층의 ISP들끼리 payment 없이 직접 연결되는 방식. 상호 주고받는 트래픽양이 유사할 때 주로 사용
- To reduce cost -> when two ISPs peer, it is typically settlement-free(no cost)
Hierarchy structure
- Access ISPs in any given region connect to regional ISP
- Regional ISP then connects to global ISP
- There may be multiple competing regional ISPs in a region
- There will be a larger regional ISP to which smaller regional ISPs in the region connect -> Multi-tier hierarchy
Content Provider Network (CPN == CDN, e.g. Google, Microsoft)
- Major content providers may run their own private network to interconnect data centers
- to reduce payment to upper-tier ISPs and get greater control of services
- 마지막에 Tier-1 ISP와 연결되어야 한다
Point of Presence (PoP)
- customer ISP가 상위 provider ISP에 연결되는 지점으로 여러 router 들의 집합
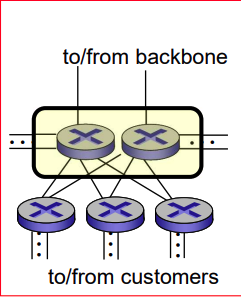
Multi-home
- ISP(except for Tier-1 ISP) may choose to connect to two or more provider ISPs
- for reliability of service
'CS > 컴퓨터네트워크' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Ch3] UDP, TCP (1) | 2023.11.21 |
|---|---|
| [Ch2 & Ch3] CDN, UDP & TCP, Mux & Demux (1) | 2023.11.14 |
| [Ch2 Application Layer] Electronic Mail, DNS, P2P applications (1) | 2023.11.02 |
| [Ch2 Application Layer] Principles of Network Applications, Web and HTTP (0) | 2023.10.30 |
| Week2: Network Performance (0) | 2023.10.20 |
